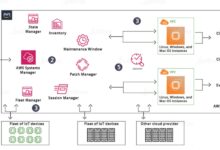
Systems manager: Systems Manager: 7 Powerful Roles and Responsibilities Revealed
If you’ve ever wondered who keeps the digital heartbeat of a company strong, look no further than the systems manager. This behind-the-scenes powerhouse ensures technology runs smoothly, securely, and efficiently across departments.
What Is a Systems Manager?

A systems manager is a critical IT professional responsible for overseeing an organization’s technological infrastructure. From servers and networks to software and security, they ensure all systems function cohesively to support business goals. Their role blends technical expertise with leadership, making them indispensable in modern enterprises.
Core Definition and Scope
The term systems manager refers to an individual who plans, coordinates, and directs activities related to computer and information systems. They are not just troubleshooters—they are strategic planners who align technology with business needs. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, these professionals often lead IT departments and make high-level decisions about tech investments.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Responsible for system architecture and integration
- Ensures uptime, scalability, and performance
- Acts as a bridge between technical teams and executive leadership
Evolution of the Role
The role of a systems manager has evolved significantly over the past two decades. Once focused primarily on maintaining servers and fixing network issues, today’s systems manager must understand cloud computing, cybersecurity, data analytics, and even artificial intelligence. The shift from on-premise infrastructure to hybrid and cloud environments has expanded their responsibilities.
“The modern systems manager isn’t just maintaining systems—they’re shaping the future of how businesses operate digitally.” — Tech Leadership Journal, 2023
This evolution reflects broader digital transformation trends across industries, from healthcare to finance.
Key Responsibilities of a Systems Manager
The day-to-day duties of a systems manager are both diverse and demanding. They must balance technical oversight with project management, team leadership, and strategic planning. Let’s explore the core areas where they make an impact.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Infrastructure Management
One of the primary functions of a systems manager is overseeing the organization’s IT infrastructure. This includes servers, storage systems, networking equipment, and cloud platforms. They ensure that all components are properly configured, updated, and optimized for performance.
- Monitor system performance and resource utilization
- Plan capacity upgrades based on usage trends
- Implement redundancy and failover mechanisms
For example, a systems manager at a mid-sized e-commerce company might use tools like Datadog or Zabbix to track server health in real time, preventing downtime during peak shopping seasons.
Security and Compliance Oversight
In an era of rising cyber threats, the systems manager plays a vital role in safeguarding organizational data. They implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption protocols, and access controls. Additionally, they ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Conduct regular vulnerability assessments
- Lead incident response during security breaches
- Train staff on cybersecurity best practices
A systems manager in the healthcare sector, for instance, must ensure that patient records are stored securely and accessed only by authorized personnel, adhering strictly to HIPAA guidelines.
Software and System Integration
Organizations rely on multiple software platforms—CRM, ERP, HR systems, etc. The systems manager ensures these systems communicate effectively through APIs, middleware, and integration platforms. Poor integration can lead to data silos, inefficiencies, and errors.
- Evaluate and select integration tools (e.g., MuleSoft, Zapier)
- Design workflows that automate cross-system processes
- Test integrations before deployment
For example, integrating Salesforce with NetSuite under the guidance of a systems manager can streamline sales-to-accounting workflows, reducing manual data entry and improving accuracy.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Essential Skills for a Successful Systems Manager
Becoming a top-tier systems manager requires more than technical know-how. It demands a blend of hard and soft skills that enable effective leadership and problem-solving in complex environments.
Technical Proficiency
A systems manager must be fluent in a wide range of technologies. This includes operating systems (Windows, Linux, Unix), virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V), cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), and networking (TCP/IP, DNS, VLANs).
- Deep understanding of system architecture and design
- Experience with scripting languages (Python, PowerShell)
- Knowledge of database management (SQL, NoSQL)
Many professionals gain these skills through certifications such as CompTIA Linux+, AWS Certified Solutions Architect, or Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Leadership and Communication
While technical skills are crucial, the ability to lead teams and communicate with non-technical stakeholders is equally important. A systems manager often reports to C-level executives and must explain complex issues in simple terms.
- Lead IT teams through change management initiatives
- Negotiate vendor contracts and manage service providers
- Present technology roadmaps to board members
Effective communication ensures that technology investments are understood and supported across the organization.
Problem-Solving and Strategic Thinking
When systems fail, the systems manager must act quickly to diagnose and resolve issues. But beyond firefighting, they must anticipate problems before they occur. This requires analytical thinking and foresight.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Use root cause analysis to prevent recurring outages
- Develop disaster recovery and business continuity plans
- Align IT strategy with long-term business objectives
For instance, a systems manager might predict increased data traffic due to a new product launch and proactively scale cloud resources to handle the load.
Systems Manager vs. IT Manager: Understanding the Difference
While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there are distinct differences between a systems manager and a general IT manager. Clarifying these roles helps organizations structure their technology leadership more effectively.
Scope of Responsibility
A systems manager typically focuses on the technical infrastructure—servers, networks, databases, and system performance. In contrast, an IT manager has a broader scope, overseeing help desk operations, user support, procurement, and sometimes even budgeting and HR functions within the IT department.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Systems manager: deep technical focus
- IT manager: broader administrative and operational oversight
In smaller companies, one person may wear both hats, but in larger organizations, these roles are often separated for efficiency.
Reporting Structure and Authority
The systems manager usually reports to the IT manager or CIO and specializes in backend systems. The IT manager, however, may have direct responsibility for all IT personnel and daily operations.
“Think of the systems manager as the architect of the digital foundation, while the IT manager is the project manager ensuring everything runs on schedule.”
This distinction becomes critical when implementing large-scale upgrades or migrations.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Specialization vs. Generalization
Systems managers are often specialists with deep expertise in specific technologies or platforms. IT managers, on the other hand, tend to be generalists who understand a wide range of IT functions but may not dive into code or server configurations.
- Systems manager: specializes in system performance, security, and integration
- IT manager: manages people, budgets, and service delivery
Both roles are essential, but they serve different purposes within the organizational hierarchy.
How to Become a Systems Manager: Education and Career Path
Becoming a systems manager is a journey that typically involves formal education, hands-on experience, and continuous learning. There is no single path, but certain steps significantly increase your chances of success.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Educational Requirements
Most systems managers hold at least a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field. Coursework often includes networking, database management, systems analysis, and cybersecurity.
- Common degrees: B.S. in Computer Science, B.S. in Information Systems
- Advanced roles may require a master’s degree (e.g., MBA with IT focus)
- Some enter the field via vocational training or bootcamps
According to BLS data, over 80% of computer and information systems managers have a bachelor’s degree or higher.
Professional Certifications
Certifications validate expertise and can accelerate career advancement. Employers often look for candidates with recognized credentials.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- CompTIA A+: Foundational IT knowledge
- CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional): For security-focused roles
- CISM (Certified Information Security Manager): Strategic security management
- PMP (Project Management Professional): For leadership and project execution
Many systems managers pursue multiple certifications throughout their careers to stay competitive.
Career Progression
Most systems managers start in entry-level IT roles such as system administrator, network technician, or help desk analyst. With experience, they move into senior technical roles before transitioning into management.
- Years 1–3: System Administrator or Network Engineer
- Years 4–6: Senior Systems Analyst or Team Lead
- Years 7+: Systems Manager or IT Operations Manager
Networking, mentorship, and taking on leadership responsibilities in projects are key to climbing the ladder.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Tools and Technologies Used by Systems Managers
Modern systems managers rely on a wide array of tools to monitor, manage, and secure IT environments. Mastery of these tools is essential for efficiency and effectiveness.
Monitoring and Performance Tools
Real-time monitoring allows systems managers to detect issues before they impact users. These tools provide dashboards, alerts, and historical data analysis.
- Nagios: Open-source monitoring for servers, switches, and applications
- SolarWinds: Comprehensive network and system monitoring
- Prometheus: Popular in cloud-native environments
These tools help identify bottlenecks, track resource usage, and generate performance reports for stakeholders.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Automation and Configuration Management
To manage hundreds or thousands of systems efficiently, automation is key. Configuration management tools ensure consistency across environments.
- Ansible: Agentless automation for provisioning and configuration
- Puppet: Declarative language for managing infrastructure as code
- Chef: Ruby-based automation platform
For example, a systems manager can use Ansible to deploy security patches across all Linux servers simultaneously, reducing manual effort and human error.
Cloud and Virtualization Platforms
With the rise of cloud computing, systems managers must be proficient in platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Manage virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions
- Configure auto-scaling and load balancing
- Implement cloud security policies
Tools like Terraform allow infrastructure to be defined in code, enabling version control and repeatable deployments.
The Future of the Systems Manager Role
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the role of the systems manager. Emerging trends are reshaping responsibilities, required skills, and career opportunities.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Automation
AI and machine learning are transforming IT operations. AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) platforms use algorithms to predict failures, automate responses, and optimize performance.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- AI-driven anomaly detection reduces mean time to resolution (MTTR)
- Chatbots handle routine user queries, freeing up IT staff
- Predictive analytics help with capacity planning
Systems managers will need to understand AI tools and integrate them into their workflows, shifting from reactive to proactive management.
Rise of DevOps and SRE Models
The traditional divide between development and operations is fading. DevOps and Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) models emphasize collaboration, automation, and continuous delivery.
- Systems managers now work closely with developers to ensure system reliability
- Emphasis on CI/CD pipelines and infrastructure as code
- Increased focus on service-level objectives (SLOs)
According to Google’s SRE book, SRE teams aim to balance innovation with stability—a goal that systems managers are uniquely positioned to support.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Remote Work and Hybrid IT Environments
The shift to remote and hybrid work models has expanded the scope of systems management. Managers must now support distributed teams, secure home networks, and cloud-based collaboration tools.
- Ensure secure access via VPNs or Zero Trust architectures
- Manage endpoint security for personal devices
- Support tools like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Slack
This trend has made cybersecurity and user experience central to the systems manager’s role.
What does a systems manager do?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
A systems manager oversees an organization’s IT infrastructure, ensuring that computer systems, networks, and software operate efficiently and securely. They lead technical teams, manage system integrations, implement security protocols, and align technology with business goals.
How much does a systems manager earn?
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for computer and information systems managers was $164,070 as of May 2023. Salaries vary based on industry, location, experience, and company size, with top earners exceeding $230,000 per year.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Is systems manager a good career?
Yes, being a systems manager is a highly rewarding career with strong job growth, competitive salaries, and opportunities for advancement. The role offers intellectual challenges, leadership responsibilities, and the chance to shape an organization’s technological future.
What certifications are best for a systems manager?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Top certifications include CISSP, CISM, PMP, AWS Certified Solutions Architect, and CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner (CASP+). These credentials demonstrate expertise in security, project management, and cloud technologies—key areas for modern systems managers.
Can a systems manager work remotely?
Yes, many systems manager roles offer remote or hybrid work options, especially in organizations with cloud-based infrastructure. However, some on-site presence may be required during critical system upgrades or emergencies.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
The role of a systems manager is more vital than ever in our digitally driven world. From ensuring system reliability to leading cybersecurity initiatives and embracing emerging technologies, they are the backbone of organizational success. Whether you’re aspiring to become one or seeking to understand their impact, recognizing the depth and breadth of this role is essential. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the systems manager—adapting, innovating, and leading the charge into the future.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: