System Development: 7 Ultimate Power Strategies for Success
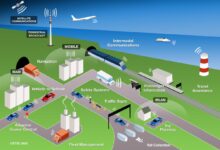
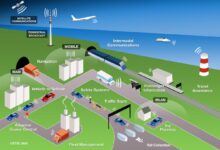
System development isn’t just about coding—it’s the backbone of modern innovation, turning ideas into powerful digital realities. From finance to healthcare, robust systems shape how we live and work. Let’s dive into the ultimate guide that breaks down every phase, method, and tool you need to master.
What Is System Development and Why It Matters

System development refers to the structured process of creating, designing, deploying, and maintaining information systems that meet specific user or business needs. It’s more than just writing software—it’s about solving real-world problems through technology, ensuring efficiency, scalability, and security.
The Core Definition of System Development
At its heart, system development is a lifecycle-driven approach to building functional systems. These systems can be software-based, hardware-integrated, or hybrid platforms designed to automate processes, manage data, or enhance decision-making. The goal is to deliver a reliable, maintainable, and user-friendly solution.
- Involves planning, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance.
- Applies to enterprise software, mobile apps, cloud platforms, and embedded systems.
- Driven by user requirements and business objectives.
Historical Evolution of System Development
The concept of system development has evolved significantly since the mid-20th century. Early systems were built using machine-level programming, with little structure or documentation. As computing grew, so did the need for organized methodologies.
- 1950s–60s: Ad-hoc programming with no formal processes.
- 1970s: Introduction of the Waterfall model by Winston Royce.
- 1980s–90s: Rise of structured analysis and design techniques (SADT).
- 2000s: Emergence of Agile, DevOps, and iterative models.
“The best systems aren’t built overnight—they’re engineered through disciplined system development practices.” — MIT Technology Review
Key Stakeholders in System Development
Successful system development involves collaboration among various stakeholders, each playing a critical role in shaping the final product.
- End Users: Define requirements and provide feedback.
- Project Managers: Oversee timelines, budgets, and team coordination.
- Developers: Write code and implement technical solutions.
- Business Analysts: Translate business needs into technical specs.
- QA Testers: Ensure quality and functionality.
The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Explained
The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is the most widely used framework for managing the creation of information systems. It provides a clear roadmap from concept to deployment and beyond, ensuring consistency, quality, and control throughout the process.
Phases of the SDLC
The SDLC typically consists of six core phases, each building upon the previous one. Skipping or rushing any phase can lead to costly errors down the line.
- Requirement Analysis: Gathering and documenting what the system must do.
- System Design: Creating architecture, interfaces, and data models.
- Implementation: Writing code and building the system.
- Testing: Validating functionality, performance, and security.
- Deployment: Releasing the system to users.
- Maintenance: Fixing bugs, updating features, and optimizing performance.
Benefits of Following SDLC
Adopting a formal SDLC offers numerous advantages for organizations aiming to deliver high-quality systems on time and within budget.
- Improved project visibility and control.
- Reduced risk of project failure.
- Better alignment between IT and business goals.
- Enhanced documentation and traceability.
- Facilitates team collaboration and accountability.
Common Pitfalls in SDLC Implementation
Despite its benefits, many teams struggle with SDLC due to poor execution or lack of adaptation.
- Insufficient requirement gathering leading to scope creep.
- Over-documentation in rigid models like Waterfall.
- Lack of user involvement during design and testing.
- Poor communication between developers and stakeholders.
- Inadequate testing resulting in post-deployment bugs.
Popular System Development Methodologies
Choosing the right methodology is crucial in system development. Different projects require different approaches based on complexity, team size, and delivery timelines. Here are the most widely used models today.
Waterfall Model: The Traditional Approach
The Waterfall model is a linear, sequential approach where each phase must be completed before the next begins. It’s one of the oldest and most structured methods in system development.
- Ideal for projects with well-defined requirements.
- Easy to manage due to rigid structure and clear milestones.
- Not suitable for dynamic environments where changes are frequent.
Learn more about the Waterfall Model at GeeksforGeeks.
Agile: The Flexible Powerhouse
Agile is a revolutionary approach in system development that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback. Instead of delivering one final product, Agile delivers working software in small, iterative cycles called sprints.
- Promotes continuous improvement and rapid adaptation.
- Encourages daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives.
- Highly effective for startups and fast-moving tech companies.
Explore the official Agile Manifesto to understand its core values.
DevOps: Bridging Development and Operations
DevOps is not just a methodology—it’s a cultural shift that integrates development (Dev) and operations (Ops) to accelerate delivery, improve reliability, and enhance collaboration.
- Automates testing, deployment, and monitoring.
- Uses CI/CD pipelines for continuous integration and delivery.
- Reduces time-to-market and increases deployment frequency.
Discover how DevOps transforms system development at Atlassian.
Key Phases in Modern System Development
While the SDLC provides a broad framework, modern system development involves deeper, more specialized phases that reflect today’s complex technological landscape.
Requirement Gathering and Analysis
This is the foundation of any successful system development project. Misunderstanding user needs at this stage can derail the entire process.
- Techniques include interviews, surveys, use case modeling, and prototyping.
- Deliverables: Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document.
- Stakeholder validation is critical before moving forward.
System Design and Architecture
Once requirements are clear, the next step is designing the system’s structure. This includes both high-level architecture and detailed component design.
- Defines modules, databases, APIs, and user interfaces.
- Chooses between monolithic, microservices, or serverless architectures.
- Ensures scalability, security, and performance from the ground up.
Implementation and Coding Standards
This is where the actual system development takes place. Developers write code based on design specifications, following best practices and coding standards.
- Use of version control systems like Git.
- Adherence to coding conventions (e.g., PEP 8 for Python).
- Code reviews and pair programming to ensure quality.
Tools and Technologies in System Development
The right tools can make or break a system development project. From planning to deployment, modern teams rely on integrated platforms to streamline workflows and boost productivity.
Project Management and Collaboration Tools
Effective communication and task tracking are essential in system development, especially in distributed teams.
- Jira: Agile project management with sprint tracking.
- Trello: Visual boards for task organization.
- Asana: Task assignment and deadline management.
- Slack: Real-time team communication.
Development and Version Control Platforms
These tools support the actual coding and collaboration among developers.
- GitHub: World’s largest code hosting platform with CI/CD integration.
- GitLab: Offers built-in DevOps tools and container registry.
- Bitbucket: Integrated with Jira for seamless workflow.
- Visual Studio Code: Lightweight, extensible code editor.
Visit GitHub to explore open-source system development projects.
Testing and Automation Frameworks
Testing ensures that the system works as intended and is free from critical bugs.
- Selenium: Automated testing for web applications.
- Jest: JavaScript testing framework for unit and integration tests.
- Postman: API testing and documentation tool.
- Jenkins: Open-source automation server for CI/CD.
Challenges in System Development and How to Overcome Them
Even with the best methodologies and tools, system development faces numerous challenges. Recognizing these early can help teams mitigate risks and deliver better outcomes.
Scope Creep and Requirement Volatility
One of the biggest threats to system development is changing requirements mid-project, often leading to delays and budget overruns.
- Solution: Use Agile sprints to accommodate changes incrementally.
- Implement change control boards to evaluate new requests.
- Set clear boundaries and prioritize features using MoSCoW method.
Technical Debt Accumulation
Technical debt refers to the implied cost of additional rework caused by choosing quick, easy solutions instead of optimal ones.
- Causes: Rushed deadlines, poor design, lack of documentation.
- Impact: Slower development, increased bugs, higher maintenance costs.
- Solution: Regular refactoring, code reviews, and automated testing.
Security and Compliance Risks
With rising cyber threats, security can no longer be an afterthought in system development.
- Integrate security early (Shift-Left Security).
- Follow standards like OWASP Top 10 for web application security.
- Ensure compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS as applicable.
Learn about secure coding practices at OWASP.
Best Practices for Successful System Development
Following proven best practices can dramatically increase the success rate of any system development initiative.
Adopt User-Centered Design Principles
Building systems around user needs leads to higher adoption and satisfaction.
- Conduct user research and usability testing.
- Create personas and journey maps.
- Design intuitive interfaces with accessibility in mind.
Implement Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD)
CI/CD automates the process of integrating code changes, running tests, and deploying to production.
- Reduces manual errors and speeds up releases.
- Enables rapid feedback and rollback capabilities.
- Tools: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, CircleCI.
Document Everything and Maintain Knowledge Sharing
Good documentation is often overlooked but is vital for long-term system maintenance.
- Document code, APIs, architecture, and deployment procedures.
- Use tools like Confluence or Notion for centralized knowledge bases.
- Encourage team wikis and onboarding guides.
Future Trends in System Development
The field of system development is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in AI, cloud computing, and automation. Staying ahead of these trends is essential for future-proofing your systems.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
AI is transforming how systems are built, tested, and maintained.
- AI-powered code assistants (e.g., GitHub Copilot).
- Automated bug detection and test generation.
- Intelligent recommendation engines in applications.
Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
These platforms allow non-developers to build applications using visual interfaces, accelerating system development for simple use cases.
- Examples: Microsoft Power Apps, Bubble, OutSystems.
- Benefits: Faster prototyping, reduced dependency on IT.
- Limitations: Limited customization and scalability.
Cloud-Native and Serverless Architectures
Modern system development increasingly relies on cloud infrastructure for scalability and resilience.
- Microservices hosted on Kubernetes or AWS ECS.
- Serverless functions (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions) for event-driven logic.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) using Terraform or CloudFormation.
What is system development?
System development is the process of creating, designing, testing, and maintaining information systems to meet specific user or business needs. It involves a structured approach using methodologies like SDLC, Agile, or DevOps to deliver functional and reliable software solutions.
What are the main phases of system development?
The main phases include requirement analysis, system design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. These phases are part of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) and ensure a systematic approach to building software.
Which methodology is best for system development?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer. Waterfall works well for stable, well-defined projects, while Agile is ideal for dynamic environments. DevOps excels in continuous delivery scenarios. The best choice depends on project scope, team size, and business goals.
How do you ensure quality in system development?
Quality is ensured through rigorous testing, code reviews, automated CI/CD pipelines, adherence to coding standards, and continuous user feedback. Implementing best practices like TDD (Test-Driven Development) also enhances reliability.
What tools are essential for modern system development?
Essential tools include GitHub for version control, Jira for project management, Jenkins for CI/CD, Postman for API testing, and Docker for containerization. The toolset varies based on methodology and team structure.
System development is a dynamic and essential discipline that powers the digital world. From defining requirements to deploying scalable systems, every phase demands precision, collaboration, and foresight. By embracing proven methodologies like Agile and DevOps, leveraging powerful tools, and staying ahead of trends like AI and cloud-native architectures, teams can build systems that are not only functional but future-ready. Whether you’re a developer, manager, or stakeholder, understanding the full spectrum of system development empowers you to drive innovation and deliver lasting value.
Further Reading: